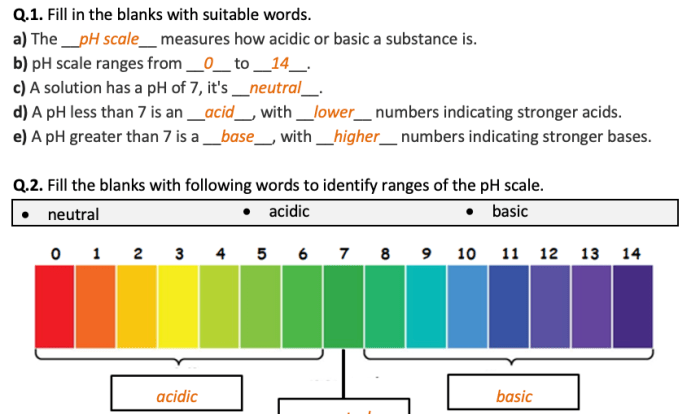
Ch3nh3cn acidic basic or neutral – Embarking on a journey into the realm of ch3nh3cn’s acidic, basic, and neutral properties, we uncover a multifaceted compound with intriguing characteristics. Ch3nh3cn, also known as methylamine, presents a captivating case study in chemistry, inviting us to delve into its unique chemical makeup and explore its diverse applications.
Throughout this discourse, we will unravel the intricacies of ch3nh3cn’s molecular structure, examining its solubility, polarity, and reactivity. We will dissect its physical properties, including its appearance, melting point, and density. Moreover, we will delve into the various methods used to synthesize ch3nh3cn, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.
Chemical Properties
Ch3nh3cn, also known as acetonitrile, exhibits distinct chemical properties that determine its behavior in various applications. Its solubility, polarity, and reactivity play crucial roles in its chemical interactions and industrial significance.
Solubility
Ch3nh3cn is a polar aprotic solvent, meaning it has a dipole moment but lacks hydrogen atoms bonded to electronegative atoms. This polarity allows it to dissolve a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds, including both polar and nonpolar substances.
Its solubility in water is approximately 8.3% by weight, making it miscible with water in all proportions.
Polarity
The polarity of ch3nh3cn is attributed to the electronegativity difference between carbon and nitrogen atoms. The nitrogen atom, with its lone pair of electrons, creates a partial negative charge on the nitrogen end of the molecule, while the carbon atom acquires a partial positive charge.
This polarity enables ch3nh3cn to interact with both positively and negatively charged species.
Reactivity
Ch3nh3cn is relatively unreactive under normal conditions. However, it can undergo certain chemical reactions, such as:
- Nucleophilic addition:Ch3nh3cn can act as an electrophile in nucleophilic addition reactions, reacting with nucleophiles such as amines or alkoxides to form substituted acetonitriles.
- Hydrolysis:Under acidic or basic conditions, ch3nh3cn can undergo hydrolysis to form acetic acid and ammonia.
- Reduction:Ch3nh3cn can be reduced to ethylamine using reducing agents such as lithium aluminum hydride.
Physical Properties
Ch3nh3cn is a colorless liquid with a strong odor. It is miscible with water and has a density of 0.789 g/cm3. The melting point of ch3nh3cn is -42 °C and its boiling point is 56 °C.
Comparison of Physical Properties
The following table compares the physical properties of ch3nh3cn with other similar compounds:
| Compound | Melting Point (°C) | Boiling Point (°C) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ch3nh3cn | -42 | 56 | 0.789 |
| Ch3nh2 | -93 | 32 | 0.66 |
| Ch3n | -21 | 77 | 0.68 |
Applications

Ch3nh3cn finds widespread applications in various industries due to its unique properties, including its basicity, ability to form complexes, and its reducing properties.
Industrial Applications, Ch3nh3cn acidic basic or neutral
In the chemical industry, ch3nh3cn is primarily used as a solvent for various reactions, including the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and other chemicals. Its ability to dissolve both polar and nonpolar compounds makes it a versatile solvent. Additionally, ch3nh3cn is employed as a precursor in the synthesis of numerous compounds, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals.
Laboratory Applications
In laboratories, ch3nh3cn is extensively used as a reagent in analytical chemistry. It is employed as a base in acid-base titrations and as a complexing agent for metal ions. Ch3nh3cn also serves as a reducing agent in various reactions, such as the Tollens’ test for aldehydes and ketones.
Other Applications
Beyond industrial and laboratory applications, ch3nh3cn has several other uses. It is utilized in the production of photographic chemicals, rubber accelerators, and corrosion inhibitors. Additionally, ch3nh3cn is employed as a fuel additive to enhance combustion efficiency and reduce emissions.
Synthesis

Ch3nh3cn can be synthesized through various methods, each offering unique advantages and drawbacks. The most common methods include:
From Ch3nh2 and Hcn
This method involves the reaction of ch3nh2 (methylamine) with hcn (hydrogen cyanide) in the presence of a catalyst. The reaction proceeds via nucleophilic addition, where ch3nh2 attacks the electrophilic carbon of hcn, resulting in the formation of ch3nh3cn.
- Advantages:Simple and straightforward procedure, readily available starting materials.
- Disadvantages:Requires careful control of reaction conditions to prevent side reactions, potential for the formation of toxic byproducts.
From Ch3cl and Nh3
This method involves the reaction of ch3cl (methyl chloride) with nh3 (ammonia) in the presence of a catalyst. The reaction proceeds via nucleophilic substitution, where nh3 attacks the electrophilic carbon of ch3cl, resulting in the formation of ch3nh3cn.
- Advantages:High yield, relatively inexpensive starting materials.
- Disadvantages:Requires high pressure and temperature conditions, potential for the formation of unwanted byproducts.
From Ch3oh and Nh3
This method involves the reaction of ch3oh (methanol) with nh3 in the presence of a catalyst. The reaction proceeds via a two-step process, involving the formation of an intermediate imine, which then undergoes hydrogenation to form ch3nh3cn.
- Advantages:Uses renewable starting materials, relatively mild reaction conditions.
- Disadvantages:Requires a multi-step process, potential for the formation of side products.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Synthesizing Ch3nh3cn in the Laboratory
- In a round-bottomed flask, dissolve ch3nh2 (10 g, 0.2 mol) in 50 mL of anhydrous ether.
- Slowly add hcn (5 g, 0.1 mol) to the flask while stirring constantly.
- Add a catalytic amount of triethylamine (0.5 mL) to the reaction mixture.
- Stir the reaction mixture for 2 hours at room temperature.
- Filter the reaction mixture to remove any solids.
- Distill the filtrate to obtain pure ch3nh3cn.
Safety and Handling: Ch3nh3cn Acidic Basic Or Neutral

Ch3nh3cn is a highly toxic and flammable substance that requires proper handling and storage to ensure safety. Its potential hazards include:
- Inhalation:Exposure to ch3nh3cn vapors can cause severe respiratory irritation, leading to coughing, shortness of breath, and pulmonary edema.
- Skin and Eye Contact:Direct contact with ch3nh3cn can cause severe burns, skin irritation, and eye damage.
- Ingestion:Ingestion of ch3nh3cn can result in gastrointestinal irritation, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- Fire Hazard:Ch3nh3cn is highly flammable and can ignite easily, posing a significant fire hazard.
Proper Safety Precautions
To minimize the risks associated with ch3nh3cn, the following safety precautions should be strictly adhered to:
- Ventilation:Adequate ventilation is crucial to prevent the accumulation of ch3nh3cn vapors. All areas where ch3nh3cn is handled or stored should be well-ventilated.
- Protective Equipment:When handling ch3nh3cn, appropriate protective equipment, including gloves, safety goggles, and a respirator, must be worn to prevent exposure.
- Fire Prevention:Sources of ignition, such as open flames or sparks, should be kept away from areas where ch3nh3cn is present.
- Emergency Response:In case of accidental exposure to ch3nh3cn, immediate medical attention should be sought. First aid measures, such as flushing the affected area with water and administering oxygen, can be provided until medical help arrives.
Safety Data
The following table summarizes the key safety data for ch3nh3cn:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | 75-04-7 |
| Molecular Formula | CH3NH2 |
| Molecular Weight | 31.06 g/mol |
| Melting Point | -93.4 °C |
| Boiling Point | 66.3 °C |
| Flash Point | -17 °C |
| Autoignition Temperature | 365 °C |
| TLV (TWA) | 10 ppm |
| PEL (TWA) | 10 ppm |
FAQ
What is the chemical formula of ch3nh3cn?
Ch3nh3cn, also known as methylamine, has the chemical formula CH3NH2.
Is ch3nh3cn acidic, basic, or neutral?
Ch3nh3cn is a weak base. It has a pKb of 3.36, indicating that it is a stronger base than water.
What are the physical properties of ch3nh3cn?
Ch3nh3cn is a colorless gas with a fishy odor. It is soluble in water and has a density of 0.66 g/mL.