A uniform plane wave propagating in a medium has captivated the minds of scientists and engineers alike, revealing a fascinating interplay of electromagnetic fields and wave characteristics. This article delves into the intricacies of this phenomenon, exploring its propagation, properties, and practical applications.
Uniform plane waves serve as a cornerstone in understanding wave behavior in various media, providing a simplified yet powerful model for analyzing wave propagation and interaction.
Propagation Characteristics

A uniform plane wave is a type of electromagnetic wave that propagates through a medium with constant amplitude and phase. It is characterized by its wave vector, frequency, and wavelength.
The wave vector is a vector that points in the direction of wave propagation and has a magnitude equal to the wavenumber. The wavenumber is related to the frequency and wavelength of the wave by the following equation:
k = 2π/λ = ω/v
where:
- k is the wavenumber
- λ is the wavelength
- ω is the angular frequency
- v is the phase velocity
The phase velocity is the speed at which a point of constant phase travels through the medium. It is determined by the properties of the medium, such as its dielectric constant and permeability.
Wave Properties
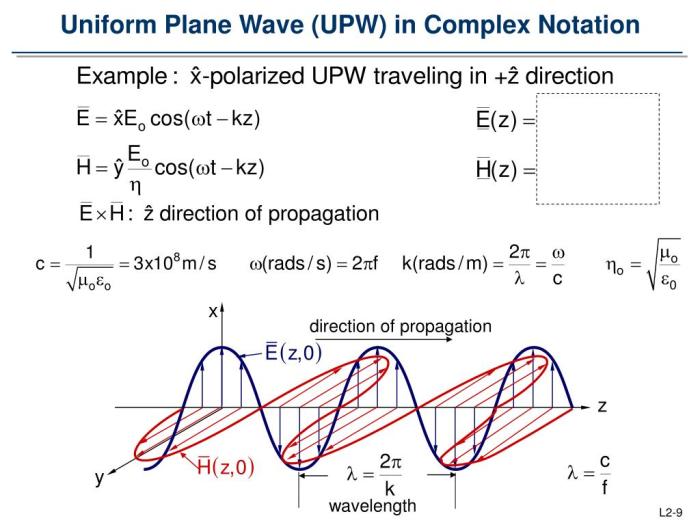
The electric and magnetic field vectors associated with a uniform plane wave are perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation. The electric field vector is given by the following equation:
E = E0e i(ωt
k·r)
where:
- E is the electric field vector
- E 0is the peak electric field amplitude
- ω is the angular frequency
- t is the time
- k is the wave vector
- r is the position vector
The magnetic field vector is given by the following equation:
B = B0e i(ωt
k·r)
where:
- B is the magnetic field vector
- B 0is the peak magnetic field amplitude
- ω is the angular frequency
- t is the time
- k is the wave vector
- r is the position vector
Polarization
The polarization of a uniform plane wave refers to the orientation of the electric field vector. There are three main types of polarization:
- Linear polarization: The electric field vector oscillates along a straight line.
- Circular polarization: The electric field vector rotates in a circle.
- Elliptical polarization: The electric field vector rotates in an ellipse.
The polarization of a wave is determined by the phase difference between the x- and y-components of the electric field vector.
Wave Propagation in Different Media
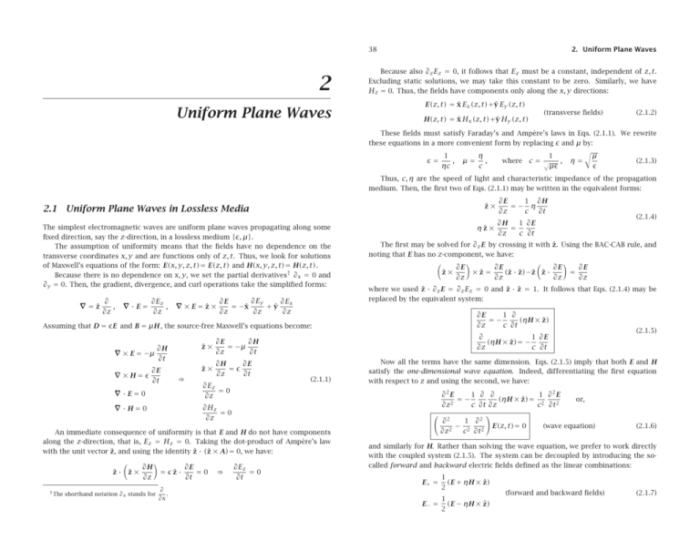
The properties of the medium through which a wave propagates can have a significant effect on the wave’s propagation characteristics. Some of the most important factors that affect wave propagation are:
- Dielectric constant: The dielectric constant of a medium determines its ability to store electrical energy.
- Permeability: The permeability of a medium determines its ability to store magnetic energy.
- Conductivity: The conductivity of a medium determines its ability to conduct electrical current.
The speed of a wave in a medium is determined by its dielectric constant and permeability.
Applications

Uniform plane waves have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Communication systems: Uniform plane waves are used in antennas to transmit and receive electromagnetic signals.
- Radar: Uniform plane waves are used in radar systems to detect and track objects.
- Medical imaging: Uniform plane waves are used in medical imaging techniques such as X-rays and MRI.
The advantages of using uniform plane waves in these applications include their ability to propagate over long distances with minimal distortion and their ability to be easily focused and directed.
FAQ Insights: A Uniform Plane Wave Propagating In A Medium Has
What is a uniform plane wave?
A uniform plane wave is an electromagnetic wave that propagates in a single direction with constant amplitude and phase over an infinite plane.
How does the frequency of a wave affect its propagation?
Frequency influences the wavelength and velocity of the wave, with higher frequencies corresponding to shorter wavelengths and faster velocities.
What is polarization, and how does it impact wave propagation?
Polarization describes the orientation of the electric field vector of a wave. It affects the interaction of the wave with matter and can be linear, circular, or elliptical.