Cell defense the plasma membrane worksheet – Embarking on a journey to unravel the intricacies of cell defense, we present the “Cell Defense: The Plasma Membrane Worksheet.” This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental role of the plasma membrane in safeguarding cells against external threats, providing a foundation for understanding the mechanisms that protect life’s building blocks.
As we navigate this worksheet, we will explore the structure and composition of the plasma membrane, its significance in maintaining membrane permeability and transport, and its involvement in cell signaling. Moreover, we will shed light on pathogen recognition and response, phagocytosis and endocytosis, and the crucial role of cell-cell communication in defense mechanisms.
1. Cell Defense
The Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane plays a crucial role in cell defense by acting as a physical barrier between the cell and its external environment. It regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell, protecting it from harmful agents.
The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins and carbohydrates. The phospholipid bilayer forms a semi-permeable barrier that allows certain substances to pass through while blocking others. The embedded proteins facilitate the transport of specific molecules across the membrane, including nutrients, ions, and waste products.
2. Membrane Permeability and Transport: Cell Defense The Plasma Membrane Worksheet
Membrane permeability refers to the ability of the plasma membrane to allow substances to pass through. It is essential for cell defense as it controls the entry of potentially harmful substances into the cell.
Membrane transport is the process by which substances are moved across the plasma membrane. There are two main types of membrane transport: passive transport and active transport. Passive transport does not require energy and involves the movement of substances down a concentration gradient.
Active transport requires energy and involves the movement of substances against a concentration gradient.
3. Cell Signaling and the Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane is involved in cell signaling, which is essential for cell defense. Cell signaling pathways allow cells to communicate with each other and respond to changes in their environment.
The plasma membrane contains receptors that bind to specific signaling molecules. When a signaling molecule binds to a receptor, it triggers a cascade of events within the cell, leading to a specific cellular response. These responses can include changes in gene expression, protein synthesis, or cell behavior.
4. Pathogen Recognition and Response
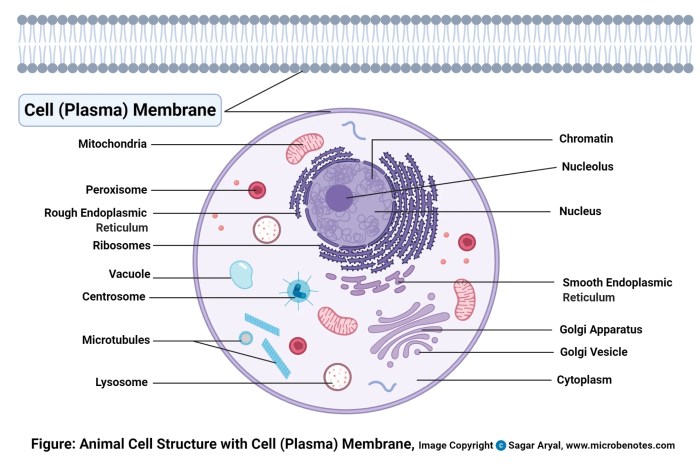
The plasma membrane plays a crucial role in pathogen recognition and response. It contains receptors that can recognize specific pathogens, such as bacteria and viruses.
When a pathogen binds to a receptor on the plasma membrane, it triggers a cellular response. This response can include the activation of phagocytes, which are cells that engulf and destroy pathogens. The plasma membrane also contains proteins that can directly kill or inhibit the growth of pathogens.
5. Phagocytosis and Endocytosis
Phagocytosis and endocytosis are two processes by which cells take in material from their surroundings. Phagocytosis is the process by which cells engulf large particles, such as bacteria and viruses. Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in small molecules and fluids.
Both phagocytosis and endocytosis are important for cell defense. They allow cells to remove pathogens and other harmful substances from their environment.
6. Cell-Cell Communication and Defense
Cell-cell communication is essential for cell defense. Cells communicate with each other through a variety of mechanisms, including direct contact, paracrine signaling, and endocrine signaling.
Direct contact involves cells physically touching each other. Paracrine signaling involves cells releasing signaling molecules that act on nearby cells. Endocrine signaling involves cells releasing signaling molecules that travel through the bloodstream to act on distant cells.
7. Applications and Implications
The role of the plasma membrane in cell defense has important implications for medicine and biotechnology. For example, understanding how the plasma membrane recognizes and responds to pathogens can lead to the development of new vaccines and therapies for infectious diseases.
Additionally, research on the plasma membrane has led to the development of new drug delivery systems that can target specific cells and tissues. These systems can be used to deliver drugs directly to the site of infection, which can improve the effectiveness of treatment and reduce side effects.
Expert Answers
What is the primary function of the plasma membrane in cell defense?
The plasma membrane acts as a selective barrier, regulating the entry and exit of substances into and out of the cell, protecting it from harmful external agents.
How does membrane permeability contribute to cell defense?
Membrane permeability allows the passage of essential nutrients while restricting the entry of harmful substances, maintaining cellular homeostasis and preventing the influx of pathogens.
What is the role of cell signaling in cell defense?
Cell signaling pathways enable cells to communicate with each other and respond to external stimuli. They play a crucial role in activating defense mechanisms and coordinating immune responses.