Acids bases & ph worksheet answers – Acids, bases, and pH are fundamental concepts in chemistry with far-reaching applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of these topics, providing a clear understanding of their properties, behaviors, and significance in our daily lives. Included within this guide are detailed answers to the acids, bases, and pH worksheet, offering valuable insights and solidifying your grasp of these essential concepts.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the defining characteristics of acids and bases, unravel the concept of pH and its measurement techniques, and delve into the practical applications of acids and bases in numerous industries. By the conclusion of this guide, you will possess a thorough understanding of these fundamental chemical principles and their impact on our world.
Acids and Bases: Acids Bases & Ph Worksheet Answers
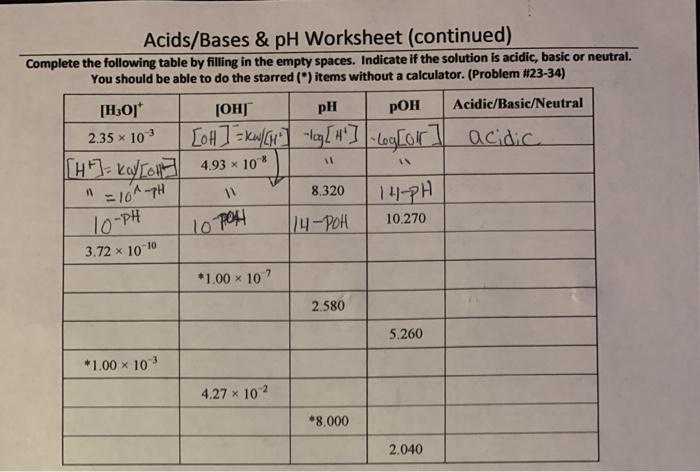
Acids and bases are two fundamental concepts in chemistry. They are defined by their properties and their behavior in chemical reactions.Acids are substances that donate protons (H+ ions) to other substances. They are typically sour to the taste, corrosive to skin, and react with metals to produce hydrogen gas.
Bases are substances that accept protons from other substances. They are typically bitter to the taste, slippery to the touch, and react with acids to produce water.
Properties of Acids and Bases, Acids bases & ph worksheet answers
The properties of acids and bases can be explained by their molecular structures. Acids typically contain hydrogen atoms that are bonded to electronegative atoms, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or chlorine. These atoms pull electrons away from the hydrogen atoms, making them more likely to be donated.
Bases typically contain atoms that have lone pairs of electrons, such as nitrogen or oxygen. These electrons can be shared with hydrogen ions, forming new bonds.The strength of an acid or base is determined by the number of protons that it can donate or accept.
Strong acids and bases donate or accept protons completely, while weak acids and bases donate or accept protons only partially.
pH
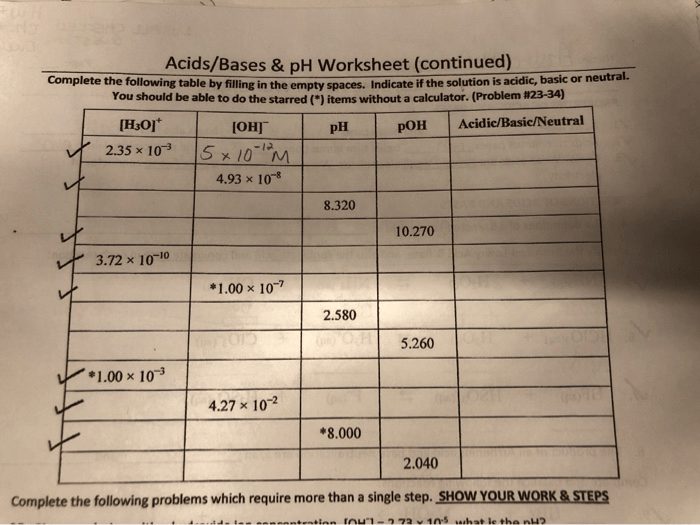
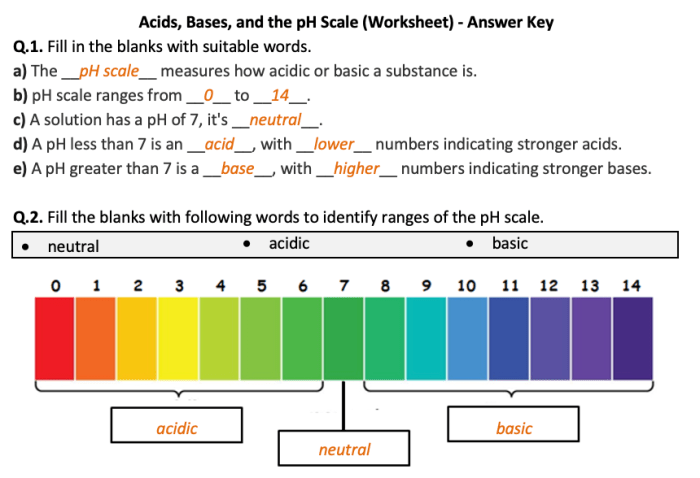
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution. It is defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most basic.
Neutral solutions have a pH of 7.pH can be measured using a pH meter or by using pH paper. pH meters are more accurate, but pH paper is less expensive and easier to use.
Acids, Bases, and pH in Everyday Life
Acids and bases are found in many everyday products, such as food, drinks, and cleaning products. The pH of these products can have a significant impact on their properties. For example, the pH of food can affect its taste, texture, and nutritional value.
The pH of cleaning products can affect their effectiveness and safety.Acids and bases are also used in a variety of industries, such as the food industry, the chemical industry, and the medical industry. In the food industry, acids and bases are used to preserve food, add flavor, and improve texture.
In the chemical industry, acids and bases are used to produce a variety of products, such as fertilizers, plastics, and pharmaceuticals. In the medical industry, acids and bases are used to treat a variety of diseases and conditions.
Quick FAQs
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid?
Strong acids completely dissociate in water, releasing all of their hydrogen ions (H+), while weak acids only partially dissociate, releasing only a fraction of their H+ ions.
How is pH measured?
pH is measured using a pH meter or pH indicator. A pH meter measures the electrical potential of a solution, while a pH indicator changes color depending on the acidity or alkalinity of the solution.
What are some examples of acids and bases found in everyday life?
Examples of acids include vinegar (acetic acid), lemon juice (citric acid), and stomach acid (hydrochloric acid). Examples of bases include baking soda (sodium bicarbonate), soap (sodium hydroxide), and ammonia.